Duo S
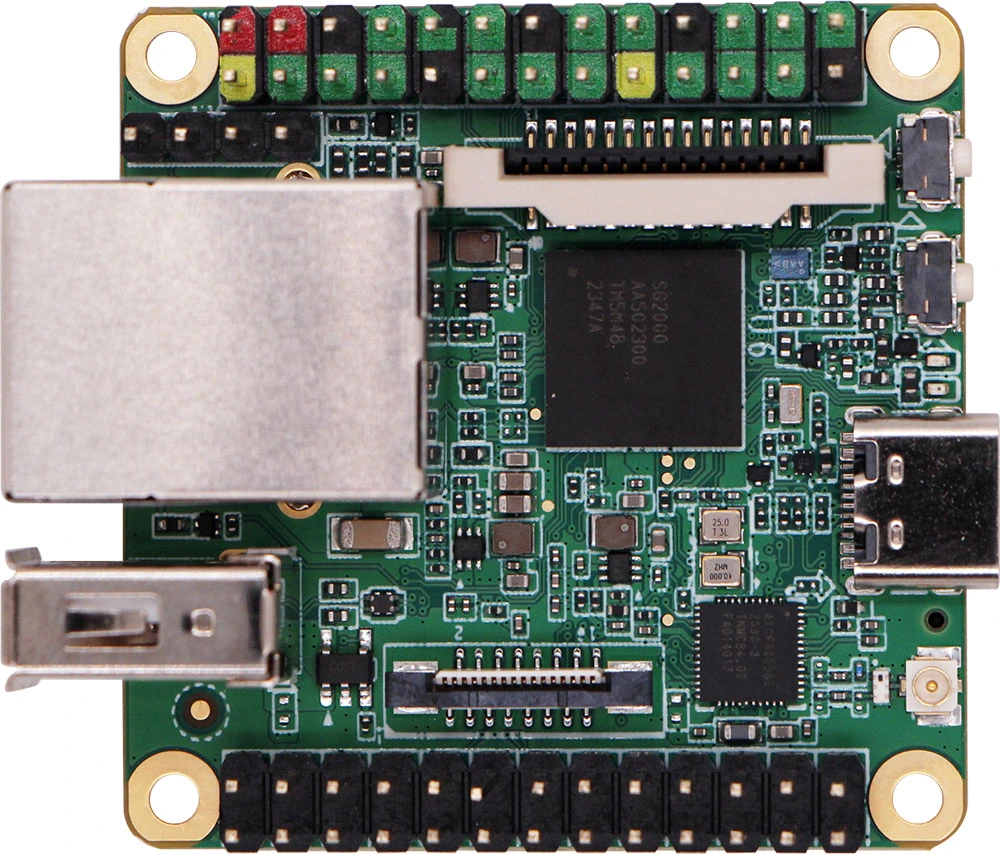
Milk-V Duo S is an upgraded model of Duo, featuring an upgraded SG2000 main controller with a larger 512MB memory and expanded IO capabilities. It integrates wireless capabilities with WI-FI 6/BT 5, and comes equipped with a USB 2.0 HOST interface and a 100Mbps Ethernet port for user convenience. Supporting dual cameras (2x MIPI CSI 2-lane) and MIPI video output (MIPI DSI 4-lane), it allows for versatile applications. The device also supports switching between RISC-V and ARM boot through a switch. With enhanced functionality, Duo S is better suited for a variety of scenarios with more complex project development requirements.
Introduction of SG2000
SG2000 is a high-performance, low-power chip designed for various product fields such as edge intelligent surveillance IP cameras, local facial recognition attendance machines, and smart home devices. It integrates H.264/H.265 video compression and decoding and ISP capabilities. It supports various image enhancement and correction algorithms like HDR wide dynamic range, 3D noise reduction, defogging, and lens distortion correction, providing customers with professional-grade video image quality.
The chip also integrates an in-house TPU, delivering approximately 0.5TOPS of computing power under INT8 operations. The specially designed TPU scheduling engine efficiently provides high-bandwidth data flow for tensor processing unit cores. It also offers users a powerful deep learning model compiler and software SDK development kit. Mainstream deep learning frameworks such as Caffe, Pytorch, ONNX, MXNet, and TensorFlow (Lite) can be easily ported to this platform.
SG2000 Public Preliminary Datasheet
We have open sourced the Public Preliminary Datasheet and TRM of SG2000 to GitHub. please check it out.
Buy the SG2000 Chips
Milk-V is the Authorised Global Distributor of the SG2000 chips. You can buy samples of the SG2000 chip from our distributor online store directly. For volume order, please contact Milk-V Sales Team for the qoutation.
Getting Started
Installing the system
-
Boot from SD card
Please refer to the Start Up section.
-
Boot from eMMC
Please refer to: eMMC version firmware burning section.
USB Network Usage
Please refer to the Setup section.
DuoS GPIO Pinout
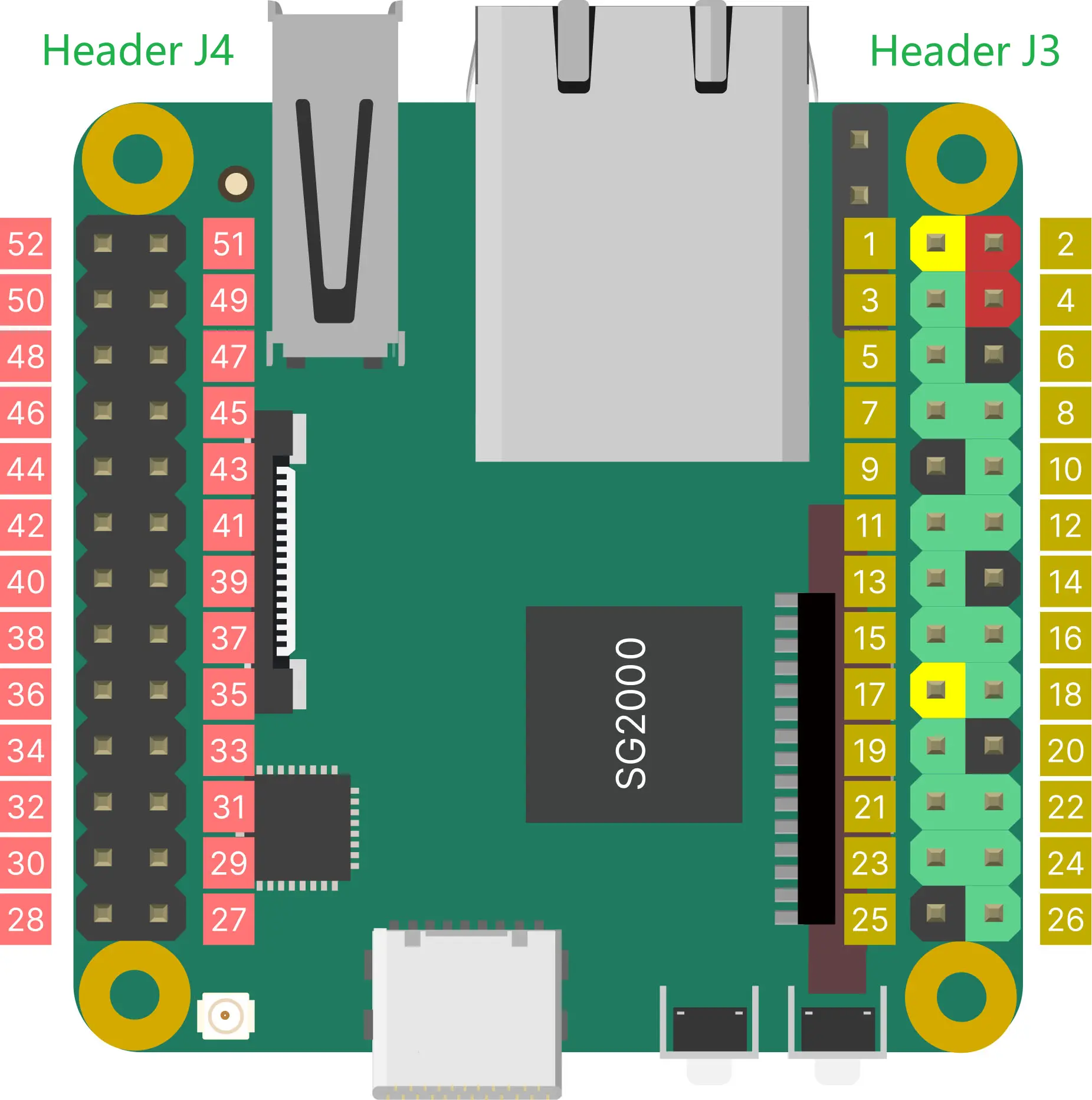
GPIO pin mapping
| GROUP | ADDR | PORT | CHIP | NUM | NAME | START |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gpio0 | gpio@03020000 | porta | gpiochip0 | 480-511 | XGPIOA | 480 - XGPIOA[0] |
| gpio1 | gpio@03021000 | portb | gpiochip1 | 448-479 | XGPIOB | 448 - XGPIOB[0] |
| gpio2 | gpio@03022000 | portc | gpiochip2 | 416-447 | XGPIOC | 416 - XGPIOC[0] |
| gpio3 | gpio@03023000 | portd | gpiochip3 | 384-415 | ||
| gpio4 | gpio@05021000 | porte | gpiochip4 | 352-383 | PWR_GPIO | 352 - PWR_GPIO[0] |
Header J3
GPIO on Header J3 use 3.3V logic levels.
| SPI | PWM | I2C | UART | NUM | SG2000 | NAME | PIN | PIN | NAME | SG2000 | NUM | UART | PWM | SPI | JTAG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3V3 | 1 | 2 | VSYS(5V) | ||||||||||||
| PWM3 | I2C4_SCL | 468 | XGPIOB[20] | B20 | 3 | 4 | VSYS(5V) | ||||||||
| I2C4_SDA | 469 | XGPIOB[21] | B21 | 5 | 6 | GND | |||||||||
| I2C1_SCL | 466 | XGPIOB[18] | B18 | 7 | 8 | A16 | XGPIOA[16] | 496 | UART0_TX/UART1_TX | PWM4 | |||||
| GND* | 9 | 10 | A17 | XGPIOA[17] | 497 | UART0_RX/UART1_RX | PWM5 | ||||||||
| PWM1 | I2C1_SDA | UART2_TX | 459 | XGPIOB[11] | B11 | 11 | 12 | B19 | XGPIOB[19] | 467 | UART2_TX | PWM2 | |||
| PWM2 | I2C1_SCL | UART2_RX | 460 | XGPIOB[12] | B12 | 13 | 14 | GND | |||||||
| UART2_RX | 470 | XGPIOB[22] | B22 | 15 | 16 | A20 | XGPIOA[20] | 500 | JTAG_TRST | ||||||
| 3V3 | 17 | 18 | A19 | XGPIOA[19] | 499 | UART1_TX/UART1_RTS | PWM7 | JTAG_TMS | |||||||
| SPI3_SDO | PWM3 | I2C2_SCL | 461 | XGPIOB[13] | B13 | 19 | 20 | GND | |||||||
| SPI3_SDI | I2C2_SDA | 462 | XGPIOB[14] | B14 | 21 | 22 | A18 | XGPIOA[18] | 498 | UART1_RX/UART1_CTS | PWM6 | JTAG_TCK | |||
| SPI3_SCK | UART2_TX | 463 | XGPIOB[15] | B15 | 23 | 24 | B16 | XGPIOB[16] | 464 | UART2_RX | SPI3_CS | ||||
| GND | 25 | 26 | A28 | XGPIOA[28] | 508 | UART2_TX/UART1_TX |
GND*: Pin 9 is a low-level GPIO in the V1.1 version of the hardware, and is GND in the V1.2 version and later.
NOTE: The I2C on the CSI camera connector J2 is I2C2, so when using the CSI camera on J2, I2C2 in the J3 pin header is not available.
Header J4
GPIO on Header J4 use 1.8V logic levels.
| PWM | I2C | UART | MIPI DSI | NUM | SG2000 | NAME | PIN | PIN | NAME | SG2000 | NUM | MIPI DSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSYS(5V) | 52 | 51 | AUDIO_OUT_R | |||||||||
| PWM12 | I2C4_SCL | UART3_TX | 449 | XGPIOB[1] | B1 | 50 | 49 | AUDIO_OUT_L | ||||
| PWM13 | I2C4_SDA | UART3_RX | 450 | XGPIOB[2] | B2 | 48 | 47 | AUDIO_IN_R | ||||
| 451 | XGPIOB[3] | B3 | 46 | 45 | AUDIO_IN_L | |||||||
| PWM10 | I2C2_SDA | LCD_RST | 354 | PWR_GPIO[2] | E2 | 44 | 43 | 3V3 | ||||
| PWM9 | I2C2_SCL | UART2_RX | LCD_PWR_CT | 353 | PWR_GPIO[1] | E1 | 42 | 41 | C18 | XGPIOC[18] | 434 | MIPI_TX_3N |
| PWM8 | UART2_TX | LCD_PWM | 352 | PWR_GPIO[0] | E0 | 40 | 39 | C19 | XGPIOC[19] | 435 | MIPI_TX_3P | |
| GND | 38 | 37 | GND | |||||||||
| MIPI_TX_2N | 436 | XGPIOC[20] | C20 | 36 | 35 | C16 | XGPIOC[16] | 432 | MIPI_TX_CN | |||
| MIPI_TX_2P | 437 | XGPIOC[21] | C21 | 34 | 33 | C17 | XGPIOC[17] | 433 | MIPI_TX_CP | |||
| GND | 32 | 31 | GND | |||||||||
| MIPI_TX_1N | 430 | XGPIOC[14] | C14 | 30 | 29 | C12 | XGPIOC[12] | 428 | MIPI_TX_0N | |||
| MIPI_TX_1P | 431 | XGPIOC[15] | C15 | 28 | 27 | C13 | XGPIOC[13] | 429 | MIPI_TX_0P |
Blue LED PIN
| NAME | SG2000 | NUM |
|---|---|---|
LED | XGPIOA[29] | 509 |
Camera interface
DuoS has two CSI camera connectors:
- J1 is a 16 PIN 0.5mm pitch connector compatible with Duo and Duo256M cameras, and can directly use the CAM-GC2083 camera.
- J2 is a 15-pin 1.0mm pitch connector compatible with the Raspberry Pi camera interface. It currently supports the OV5647 camera used on the Raspberry Pi.
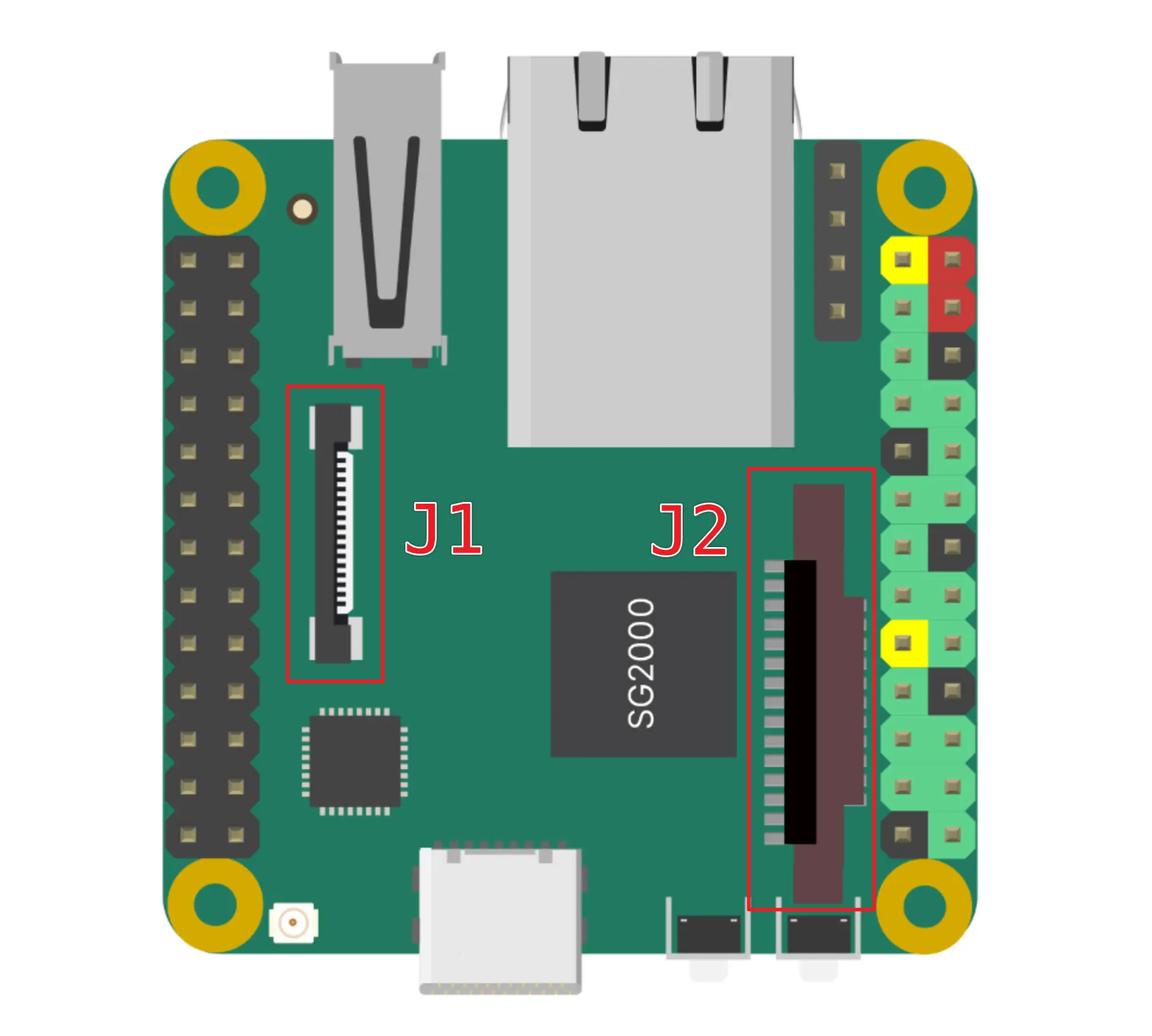
Note that the I2C used by the J1 interface is I2C3, and the I2C used by the J2 interface is I2C2. Please check the pin multiplexing configuration when using it.
J1 Connector FPC Definition
| J1 | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | GND |
| 2 | MIPI0_DN0 |
| 3 | MIPI0_DP0 |
| 4 | GND |
| 5 | MIPI0_DN1 |
| 6 | MIPI0_DP1 |
| 7 | GND |
| 8 | MIPI0_CKN |
| 9 | MIPI0_CKP |
| 10 | GND |
| 11 | SENSOR_RSTN0 (1.8V) |
| 12 | SENSOR_CLK0 (1.8V) |
| 13 | I2C3_SCL (1.8V) |
| 14 | I2C3_SDA (1.8V) |
| 15 | |
| 16 | 3V3 |
J2 Connector FPC Definition
| J2 | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3V3 |
| 2 | I2C2_SDA (3.3V) |
| 3 | I2C2_SCL (3.3V) |
| 4 | SENSOR_CLK1 (3.3V) |
| 5 | SENSOR_RSTN1 (3.3V) |
| 6 | GND |
| 7 | MIPI0_DP5 (CAM1_CP) |
| 8 | MIPI0_DN5 (CAM1_CN) |
| 9 | GND |
| 10 | MIPI0_DP4 (CAM1_DP1) |
| 11 | MIPI0_DN4 (CAM1_DN1) |
| 12 | GND |
| 13 | MIPI0_DP3 (CAM1_DP0) |
| 14 | MIPI0_DN3 (CAM1_DN0) |
| 15 | GND |
POE Header
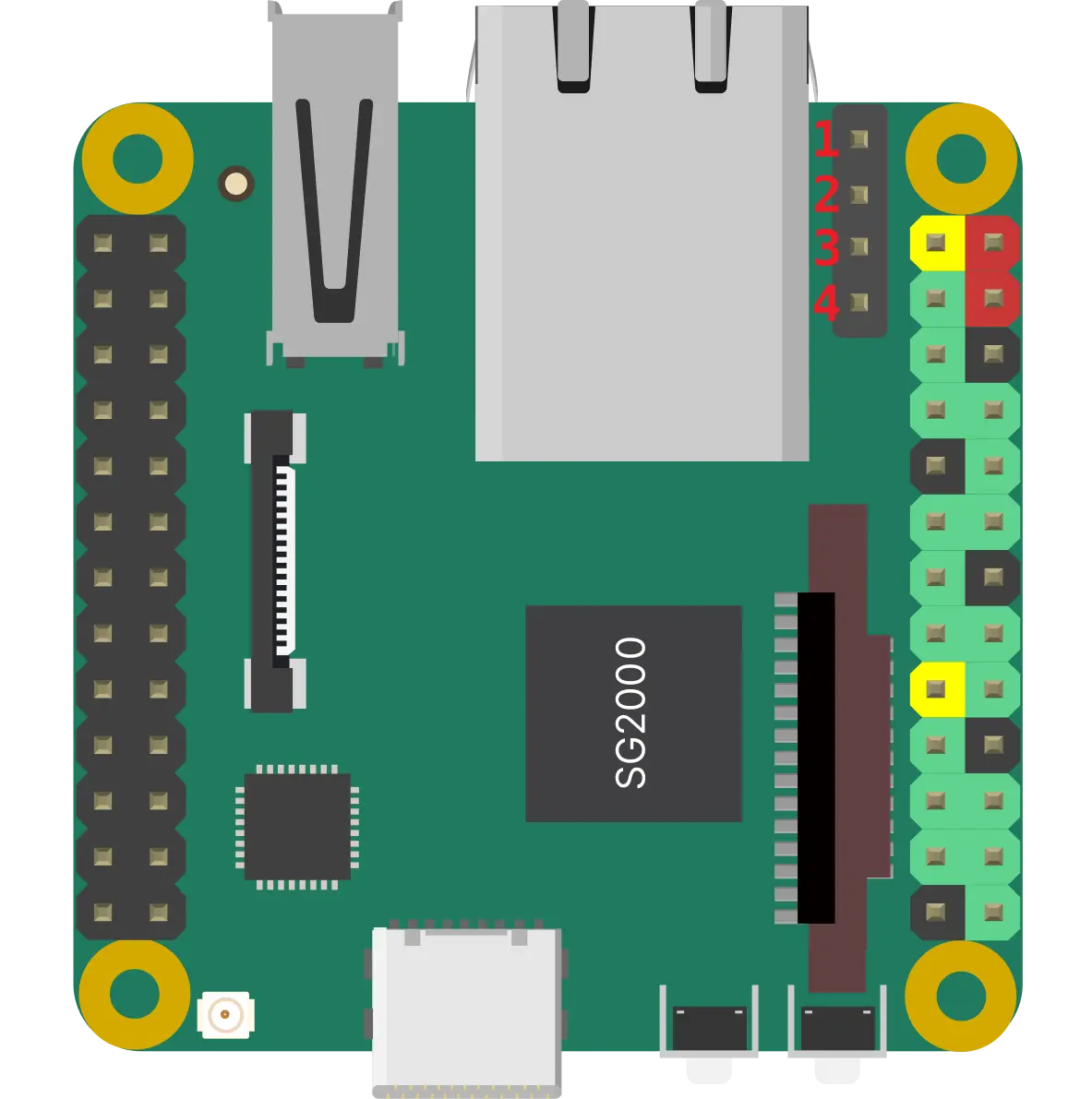
| POE Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | VB- |
| 2 | VB+ |
| 3 | VA- |
| 4 | VA+ |
DuoS User Guide
RISC-V and ARM switching
The large core of DuoS can choose to use RISC-V or ARM processor, which can be set through the switch on the board. If you find that DuoS cannot start normally during use, please first check whether the switch is consistent with the firmware used.
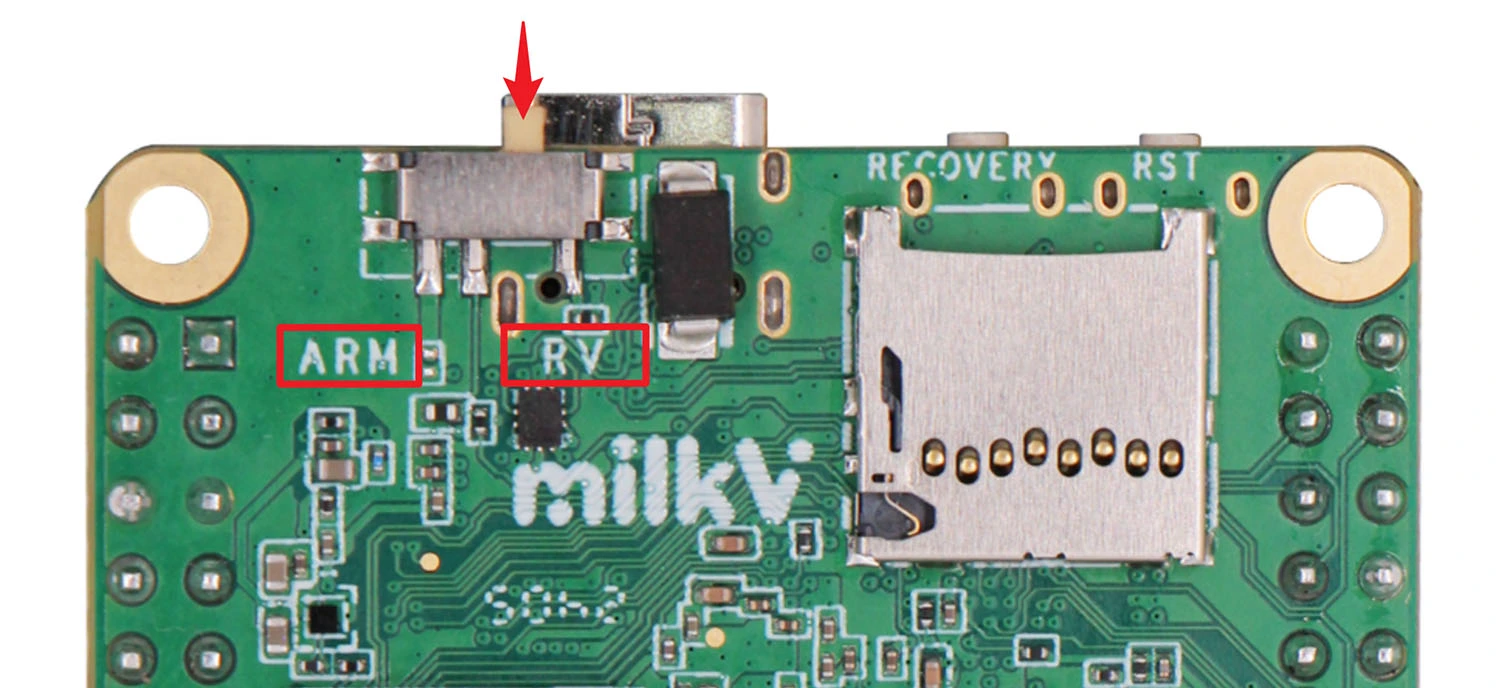
If the debug serial port is connected, you can see in the first line of the boot log that starting with C means starting from the RISC-V core, and starting with B means starting from the ARM core.
- RISC-V:
C.SCS/0/0.C.SCS/0/0.WD.URPL.USBI.USBW - ARM:
B.SCS/0/0.WD.URPL.B.SCS/0/0.WD.URPL.USBI.USBW
Usage of USB Type A interface
The USB functions of the DuoS USB Type A interface and Type C interface are optional and cannot be used at the same time. The default firmware is configured with the USB network port (USB-NCM) function of the Type C port. If you need to switch to the USB 2.0 HOST port of the Type A port for use with USB flash drives and other devices, you need to execute the following command:
ln -sf /mnt/system/usb-host.sh /mnt/system/usb.sh
sync
Then execute the reboot command or power on again to make it take effect.
For example, after connecting a USB flash drive to the USB A port, you can use ls /dev/sd* to check whether the device is detected.
Mount it to the system to view the contents of the USB flash drive (take /dev/sda1 as an example):
mkdir /mnt/udisk
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/udisk
Check whether the contents of the /mnt/udisk directory are as expected:
ls /mnt/udisk
Command to uninstall USB flash drive:
umount /mnt/udisk
When you want to restore the USB network (USB-NCM) function of the Type C port, execute:
rm /mnt/system/usb.sh
ln -sf /mnt/system/usb-ncm.sh /mnt/system/usb.sh
sync
Then execute the reboot command or power on again to make it take effect.
DuoS has an onboard Ethernet interface, so the USB network port (USB-NCM) of the Type C port can be used without switching to the USB 2.0 Host function of the A port.
Fixed ethernet port MAC address
If you need to assign a fixed MAC address to the Ethernet port of DuoS, please execute the following command:
Replace the MAC address in the command with the MAC address you want to set, and please note that MAC addresses of different devices within the same network segment must not be duplicated
echo "pre-up ifconfig eth0 hw ether 78:01:B3:FC:E8:55" >> /etc/network/interfaces && sync
then reboot the board.
UART Serial Console
DuoS has a reserved UART debug serial port, which can be used to view the system startup log, or to log in to the console after the system starts and execute some terminal commands.
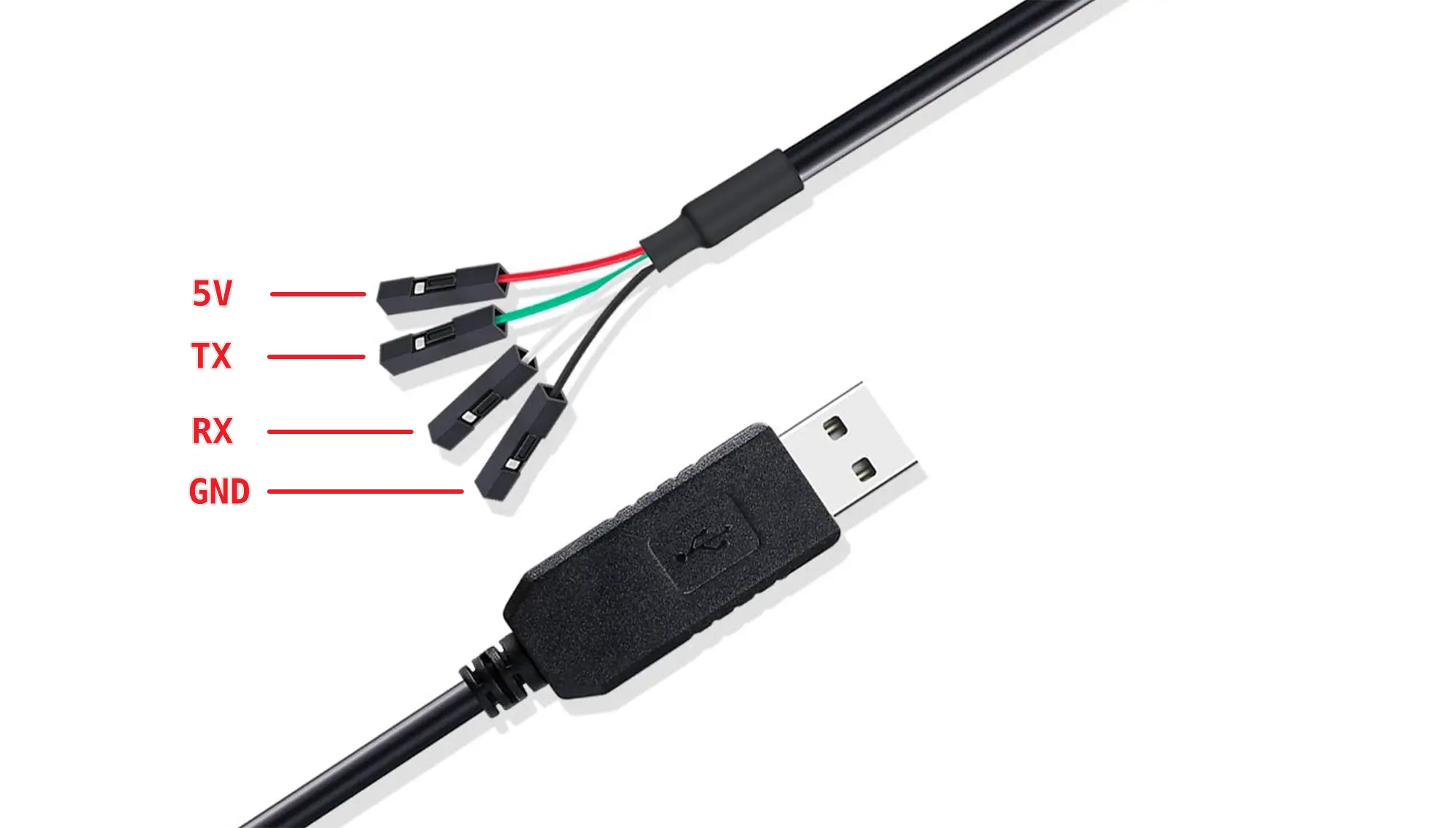
USB-TTL Serial Cable
The serial port level of Duo series is 3.3V.
The pin definitions of common USB to TTL serial cables are as follows:

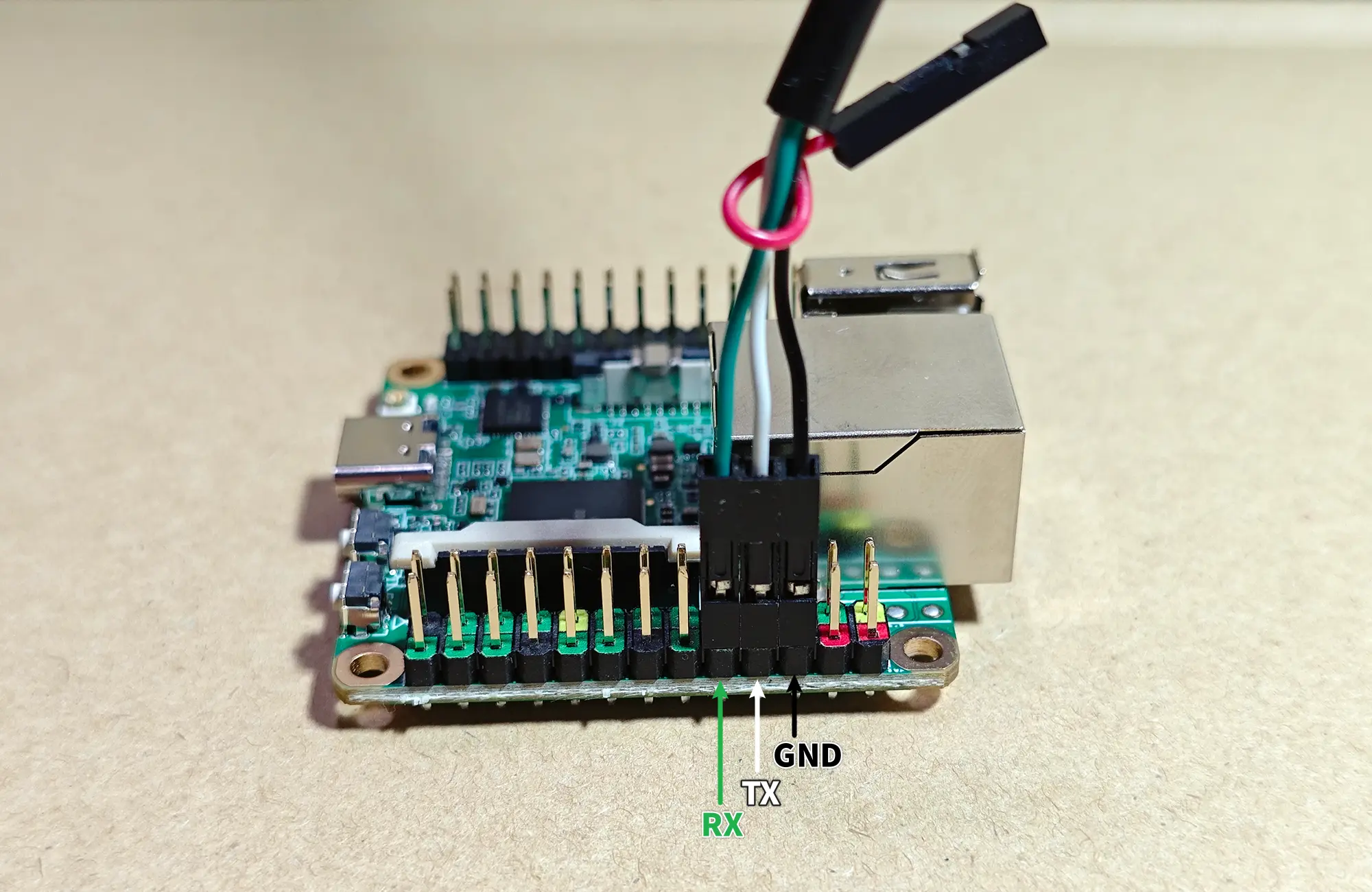
Connection
Connect the USB to TTL serial cable as shown below, leaving the red wire unconnected.
| Milk-V DouS | <---> | USB to TTL |
|---|---|---|
| GND (pin 6) | <---> | Black wire |
| TX (pin 8) | <---> | White wire |
| RX (pin 10) | <---> | Green wire |
The default serial port parameters of DuoS are as follows:
baudrate: 115200
data bit: 8
stop bit: 1
parity : none
flow control: none
WIFI configuration
Method 1
Edit the following file and replace ssid and psk with the WIFI account and password to be connected:
ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant
ap_scan=1
update_config=1
network={
ssid="wifi_test"
psk="12345678"
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
}
Then execute the following command:
wpa_supplicant -B -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
You can connect to WIFI. After connecting, you can view the assigned IP address through the ifconfig or ip a command.
If you need to automatically connect to the WIFI when booting, you can put the following command in the /mnt/system/auto.sh file.
interface="wlan0"
max_attempts=100
attempt=0
log_file="/var/log/auto.sh.log"
# Continuously attempt to detect if the interface exists, up to $max_attempts times
echo "start auto.sh" > "$log_file"
while [ $attempt -lt $max_attempts ]; do
# Check if the wlan0 interface exists
ip link show "$interface" > /dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "$(date +'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') $interface interface exists, starting wpa_supplicant..." >> "$log_file"
wpa_supplicant -B -i "$interface" -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf >> "$log_file"
break # Exit the loop if the interface is found
else
echo "$(date +'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') $interface interface not found, waiting..." >> "$log_file"
sleep 1 # Wait for 1 second before checking again
attempt=$((attempt + 1)) # Increment the attempt counter
fi
done
# If the maximum number of attempts is reached and the interface still not found, output an error message
if [ $attempt -eq $max_attempts ]; then
echo "$(date +'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') Interface $interface not found after $max_attempts attempts" >> "$log_file"
fi
Fixed WIFI MAC address
DuoS WIFI MAC address is randomly assigned. If you need to assign a fixed MAC address to the WIFI of DuoS, please execute the following command::
Replace the MAC address in the command with the MAC address you want to set, and please note that MAC addresses of different devices within the same network segment must not be duplicated
echo "MAC_ADDR=11:22:33:44:55:66" > /mnt/system/firmware/aic8800/rwnx_settings.ini && sync
then reboot the board.
eMMC version firmware burning
The DuoS eMMC version does not have firmware burned and needs to be burned using a PC through the USB interface.
Use the USB burning tool under Windows to support eMMC. The firmware version is V1.1.3 or latest version.
Burning in Windows
-
Install driver
Download the USB driver installation tool: CviUsbDownloadInstallDriver.zip. After downloading, unzip and install.
-
Download burning tool
Download the command line burning tool under Windows CviBurn_v2.0_cli_windows.zip, unzip it after downloading.
-
Download firmware
Download the latest version of DuoS eMMC firmware, currently milkv-duos-emmc-v1.1.3-2024-0930.zip, you can create a new rom folder in the burning tool
CviBurn_v2.0_cli_windowsdirectory, and extract the downloaded eMMC firmware compressed package to rom directory, the directory structure of the burning tool is as follows:└───CviBurn_v2.0_cli_windows
│ cv_dl_magic.bin
│ usb_dl.exe
└───rom
│ boot.emmc
│ fip.bin
│ partition_emmc.xml
│ rootfs_ext4.emmc
| ...In the Windows terminal, execute the burning command in the
CviBurn_v2.0_cli_windowsdirectory:.\usb_dl.exe -s linux -c cv181x -i .\rom*You can also put the firmware in other directories and specify the corresponding directory through the -i parameter in the command. *
Displays message waiting for USB connection:
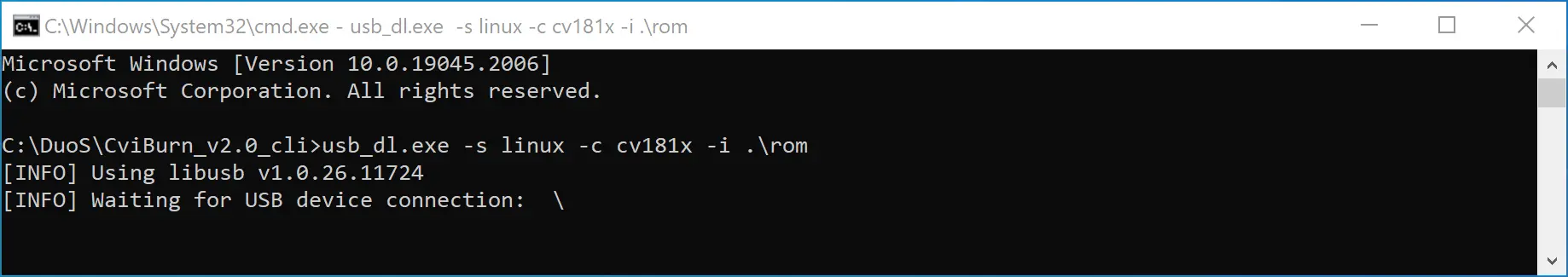
Press and hold the recovery button on the DuoS, and then connect the DuoS and PC using a Type-C data cable.
warningBefore doing this step, remove SD Card first!!

Release the recovery button, DuoS will power on and enter the burning mode, and the PC will display the burning progress in real time:
[INFO] Waiting for USB device connection: ---
[INFO] found usb device vid=0x3346 pid=0x1000
[INFO] downloading file: .\rom\boot.emmc
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 3384664/213100824(1%)
[INFO] downloading file: .\rom\rootfs_ext4.emmc
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 20161944/213100824(9%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 36939224/213100824(17%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 53716504/213100824(25%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 70493784/213100824(33%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 87271064/213100824(40%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 104048344/213100824(48%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 120825624/213100824(56%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 137602904/213100824(64%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 154380184/213100824(72%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 171157464/213100824(80%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 187934744/213100824(88%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 204712024/213100824(96%)
[INFO] CVI_USB_PROGRAM
[INFO] updated size: 213100696/213100824(99%)
[INFO] USB download completeAfter the burning is completed, the DuoS will automatically restart. After booting, you will see the blue LED on the DuoS flashing, indicating that the system has started normally and the burning is successful.
eMMC Erase
If you need to restore the eMMC to its initial state, please refer to the following command to clear the eMMC data (please back up important files in the eMMC in advance):
- Unlock readonly
echo 0 > /sys/block/mmcblk0boot0/force_ro
echo 0 > /sys/block/mmcblk0boot1/force_ro - Erase
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/mmcblk0boot0 bs=1M count=4
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/mmcblk0boot1 bs=1M count=4
